Benchmark
Problems
Benchmark Problem B1-4F
-Properties-
|
category
|
type
|
index
|
domain
|
object
|
note
|
B. interior
|
1. practical
|
B1-4F
|
frequency
|
reverberation room
|
scattering
|
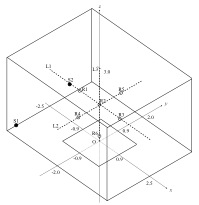 Geometry:
Geometry: Rectangular room (5 m x 4 m x 3 m) with an absorbing material (1.8 m x 1.8 m x 0.05 m or 0.1 m ) and a point source. The absorbing material is modeled as flat surface.
Boundary condition:
All faces are assumed to be rigid except for a sound absorbing material on a floor. As the sound absorbing material, a glass wool with density of 32 kg/m3 is located in the center part on the floor. The locally-reactive boundary condition is assumed on the material surface and the surface impedance of the glass wool with rigid-back wall is given here. A point source is located at two positions S1(-2.3, -1.8, 0.2) or S2(-1.5, 0.0, 1.5), assuming its stationary vibration with volume acceleration amplitude 1.0 m3/s2.
Fig. B1-4F-1:
Geometry of problem B1-4F (unit: m).
-Task A-
Frequency response:
Sound pressure amplitude [Pa] at 6 points (-1.0, 0.0, 1.5) (R1), (0.0, 0.0, 1.5) (R2), (1.0, 0.0, 1.5) (R3), (0.0, -1.0, 1.5) (R4), (0.0,1.0, 1.5) (R5), (0.0, 0.0, 0.2) (R6). At the frequencies with 1 Hz intervals from 20 Hz to 4 kHz; or with 10 Hz intervals from 20 Hz to 4 kHz.
Dataform:
d-b1-4fa.xls
Contribution:
-Task B-
Distribution:
Sound pressure amplitude [Pa] at 243 points on the 3 lines(L1, L2, L3), L1: y = 0, z = 1.5 located at 0.05 m intervals (x = -2.5, …, 2.5) , L2: x = 0.0, z = 1.5 located at 0.05 m intervals (y = -2.0, …, 2.0), L3: x = 0.0, y = 0.0 located at 0.05 m intervals (z = 0.0, …, 3.0). At the one-third octave-band mid-frequencies (f = 31.5, 63, 125, 250, 500, 1k, 2k, 4k Hz)
Dataform:
d-b1-4fb.xls
Contribution: