Benchmark
Problems
Benchmark Problem A1-5F
-Properties-
|
category
|
type
|
index
|
domain
|
object
|
note
|
A. exterior
|
1. practical
|
A1-5F
|
frequency
|
Absorptive barrier with cylindrical edge
|
diffraction
|
Geometry:
A barrier on the rigid ground. A circular cylinder of 0.5 m diameter is attached to the edge of the barrier, and total barrier height including the cylinder is 3.0 m. Thickness of straight barrier part is 0.1m.
Boundary condition:
Barrier surface (both the cylindrical edge and the straight barrier part) are absorptive boundaries, i.e., rho * c impedance surfaces, and the ground surface is a rigid boundary. A sound source (S) is located on the ground surface at a horizontal distance of 5.0 m from the barrier.
Optional condition:
Some options are offered to contributors in the following conditions; barrier thickness of straight barrier part, barrier length, and source shape. Thickness of straight barrier part is recommended to be 0.1 m, or approximated to infinitesimal if necessary to implement calculations. Barrier length should be infinite in two-dimensional calculation, or finite with an arbitrary length in three-dimension. Regarding source shape, there are three options: a coherent line source, a incoherent line source and a point source. The both line sources should be located at (x, y) = (-5.0, 0.0), while the point source should be located at (x, y, z) = (-5.0, 0.0, 0.0). Contributors can choose calculating conditions from the above, and adopted conditions must be specified in the "Comment on Result" field of the "Result" sheet.
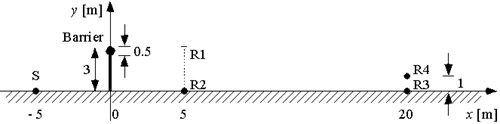
Fig. A1-5F-1: Geometry of problem A1-5F (unit: m).
-Task A-
Spatial distribution:
Insertion loss* [dB] of the barrier at 151 points (R1) on the line (x, z) = (5.0, 0.0), located at 0.02 m intervals (y = 0.00, 0.02, 0.04, ..., 3.00). At the octave-band mid-frequencies (f = 31.5, 63, 125, 250, 500, 1k, 2k, 4k Hz).
Dataform:
d-a1-5fa.xls
Contribution:
- [05/03/07] A1-5FA-03: 2D-BEM (Burton & Miler method), Okubo, T.
- [04/10/17] A1-5FA-02: 2D-BEM (Basic Form with internal absorbing hollow), Okubo, T.
- [04/10/17] A1-5FA-01: 2D-BEM (Basic Form), Okubo, T.
-Task B-
Frequency characteristics:
Insertion loss* [dB] of the barrier at 3 points; R2 at (5.0, 0.0, 0.0), R3 at (20.0, 0.0, 0.0) and R4 at (20.0, 1.0, 0.0). At the frequencies with 1 Hz intervals from 20 Hz to 4 kHz; or with 50 Hz intervals from 50 Hz to 4 kHz.
Dataform:
d-a1-5fb.xls
Contribution:
- [05/03/07] A1-5FB-03: 2D-BEM 2D-BEM (Burton & Miler method), Okubo, T.
- [04/10/17] A1-5FB-02: 2D-BEM 2D-BEM (Basic Form with internal absorbing hollow), Okubo, T.
- [04/10/17] A1-5FB-01: 2D-BEM (Basic Form), Okubo, T.
Ref. comparison and discussion (presentation materials for the symposium on March 4, 2005)
* Insertion loss (IL) [dB] is defined as follows:
IL = SPLbefore - SPLafter [dB]
SPLbefore [dB] : sound pressure level with only the ground present.
SPLafter [dB] : sound pressure level with both the barrier and the ground present.